Pharmacogenetics Roll Out – Gauging Response to Service (PROGRESS) programme looks to establish the feasibility of providing an NHS-wide diagnostic service to identify genetic changes associated with commonly prescribed drugs.
Medicines are the most common therapeutic intervention in healthcare, yet the efficacy and safety of many drugs show considerable interpersonal variation. Some patients have been prescribed medication that does not work well, whereas others develop reactions to their medicines. Sub-optimal medicines use is a globally important problem that costs lives and large sums of money. This project will
- develop and validate an initial genetic test for NHS use
- develop a system to translate the laboratory findings into prescribing advice for use in primary care (GPs)
- work with a small number of GPs across the North West to test the system
- investigate the healthcare economics and implementation strategy to ensure the test is affordable for the NHSE and the way it can be adopted
- work with patient groups across England to understand how patients feel about this type of testing
BSL version
The NW Clinical Lead for this project is Professor Bill Newman, Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust
The Pharmacogenetics Roll Out – Gauging Response to Service [PROGRESS] programmee is an NHS England (NHS-E) Funded transformation project led by researchers at the NHS Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust (MFT) and the NHS NW Genomic Medicine Service Alliance (NWGMSA), to investigate the feasibility of delivering pre-emptive pharmacogenetic panel testing in primary care in the NHS
It has been split into three distinct work packages, each of which deals with a different aspect of the programme.
Pharmacogenetics describes how we can leverage the knowledge of an individual’s genetic information to support medicines optimisation, better-informing medicine selection, and dosing.
Work Package 1 has focussed on the validation of the pharmacogenetic testing technology, involving a lab scientist at the NHS NW Genomic Laboratory Hub (NWGLH) assessing a number of commercially available pharmacogenetic panels to determine the appropriate choice for the clinical trial, based on factors including the robustness of testing, cost and turnaround time.
In Work Package 2 we have worked with health informaticians and digital experts to run a series of workshops with primary care doctors and pharmacists to develop an informatic solution that can communicate the results of the pharmacogenetic testing from the NWGLH to the primary care team. Initially, this will be through a standalone interface that will need to be logged in to, when informed that patients’ results are back, but later we aim to deliver that result directly into the EPR system used in the practice, e.g., EMIS or System One.
Work Package 3 is the PROGRESS Clinical Trial, a portfolio-adopted study, which will test the feasibility of delivering these pharmacogenetic results for real patients in primary care in the NHS and provide genotype-guided prescribing. Phase 1 of the PROGRESS Clinical Trial will initially begin at five primary care networks (PCNs) in the North West of England. Recruitment started in Summer 2023.
Patients who are being seen for a new prescription of one of the following classes of medicines will be invited to participate in the study: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), statins or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). They would then provide a blood sample which is sent to the NWGLH for testing and the results will be returned to the primary care team in 7 to 10 working days. The patient’s own primary care team will then be able to incorporate this guidance to inform the patient’s prescription.
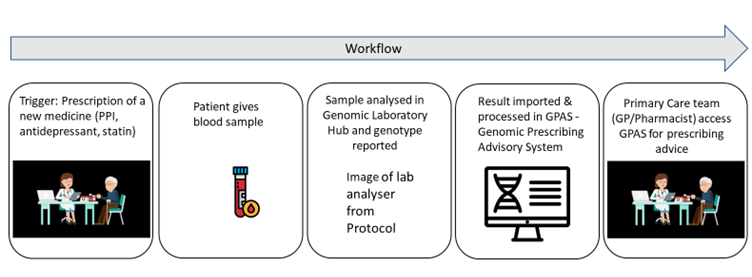
For example, the patient may have attended with low mood and a prescription of citalopram was considered. If their pharmacogenetic results show that they are a CYP2C19 ultrarapid metabolsior, the system would recommend an alternative antidepressant which is more likely to be efficacious.
This will generate some useful evidence around the feasibility of delivery in primary care and the aim is to scale during 2023 to an extended national pilot with additional practices from other GMSA regions across England. Ultimately this will feed into national commissioning decisions about how we implement pharmacogenetics in the NHS
The NHS North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance (NW-GMSA) is pleased to announce the launch of Phase II of the PROGRESS (Pharmacogenetics Roll Out – Gauging Response to Service) research study, marking the national rollout across England of ProgressRX.
The PROGRESS project seeks to establish the feasibility of providing an NHS-wide diagnostic service to identify genetic changes associated with commonly prescribed drugs. Pharmacogenomics examines how an individual's genetic makeup influences their response to medications.
Phase II is broadening the study’s reach, with recruitment now extending across England and the introduction of ProgressRx, a cutting-edge digital tool designed to integrate pharmacogenomic results directly into prescribing systems.
Introducing ProgressRx
ProgressRx is an "end-to-end diagnostic interpretation tool" that seamlessly translates genomic test results into practical prescribing advice. It integrates into existing NHS clinical decision support (CDS) systems, reducing the cognitive burden on prescribers while providing real-time, patient-specific guidance.
CDS provides timely information, usually at the point of care, to help inform decisions about a patient's care. CDS tools and systems help clinical teams by taking over some routine tasks, warning of potential problems, or providing suggestions for the clinical team and patient to consider.
Tailoring drug therapies based on genetic profiles, healthcare providers can minimise adverse drug reactions and optimise therapeutic outcomes; by integrating pharmacogenomic testing into routine NHS care, medication safety and effectiveness for patients across England will be enhanced.
Key enabler stakeholders
Phase II of the PROGRESS project has been made possible through collaboration with enabler stakeholders specialising in clinical decision support systems:
Clinical Architecture (CA) is a leader in healthcare terminology management and interoperability solutions. It provides advanced tools that enhance data quality and support clinical decision-making by ensuring that healthcare information is clear, accurate, and accessible. Learn more
FDB (First Databank) delivers comprehensive drug databases and clinical decision support solutions that integrate into healthcare systems, helping doctors and pharmacists make safe and effective medication decisions. Their OptimiseRx system enables real-time, patient-specific clinical decision support within the Primary Care Patient Record, for example EMIS or SystmOne. Learn more
Collaboration in action
The Phoenix Partnership’s (TPP) SystmOne facilitates sharing of electronic patient records across various healthcare settings, ensuring that healthcare professionals have access to the same up-to-date information wherever the patient seeks treatment. TPP have contributed to the project and informed its development.
Ongoing collaboration ensures that pharmacogenomic data is effectively incorporated into clinical workflows, providing actionable insights to healthcare professionals at the point of care.
By leveraging existing innovations within clinical decision support, the PROGRESS project is set to personalise medication regimens, minimise adverse drug reactions, and improve patient outcomes across the NHS.
Advancing precision medicine
The national rollout of Phase II signifies a significant step towards embedding genomics into routine NHS healthcare, advancing precision medicine, and improving medication safety and efficacy.
The Pharmacogenomics and Medicines Optimisation Network of Excellence looks forward to sharing outcomes from the research study; to highlight the transformative impact this initiative could have on patient care across England. Learn more
What does PROGRESS mean for patients?
We know that medicines are not always effective for many patients, or that some patients may experience harmful side effects while others do not. This can be due to several factors but one reason can be because of differences in our DNA, known as genetic variation. Pharmacogenetics is the study of how a person’s genes affect their response to medicines. PROGRESS is the first study to focus on how to deliver a pharmacogenetics service within the NHS. In practice, this means that a patient on the study will undergo a simple blood or saliva test when they see their GP before being prescribed a new medicine. Once the results are available, the GP or pharmacist at the surgery will be able to access bespoke prescribing recommendations so that any treatment is tailored to the person’s individual genetic profile. Importantly, the test only needs to be done once in a patient’s lifetime and the results will be available for healthcare professionals to help decide the best medicines for them now, and in the future.
Patients who take part in the study will play a hugely important role in shaping the future of healthcare in the NHS. If the study is successful, it could mean that pharmacogenetics will become a normal part of NHS healthcare, leading to improved safety and effectiveness of many commonly prescribed medicines.
The PROGRESS study signifies a paradigm shift in how we make prescribing decisions and treat patients with medicines, to create a system that makes pharmacogenetics a normal part of healthcare. The availability of this information will represent another tool to support medicines optimisation.
Pharmacy professionals, as experts in medicines, will be critical to making this a success and will have a wide range of key roles to play. Those who are involved with the study itself can identify patients for inclusion, for example through routine medication reviews. Practice pharmacists may also be the nominated healthcare professional who is notified of the genetic test results and to action any changes to the prescription. Similarly, they may expect to support clinicians and other practitioners with interpreting the results in the context of an individual patient, advising on prescribing decisions, monitoring requirements, or alternative treatments.
Looking to the future, if pre-emptive panel testing becomes adopted into routine healthcare across the NHS, results will need to be saved in patient medical records so that they will be available for use for prescribing decisions across all healthcare settings. These results will also need to be in a clinically relevant format for healthcare professionals to use without the need for specialist training. Pharmacists will need to be able to incorporate pharmacogenetic information that may have been requested months or years previously, for a new clinical scenario. Providing appropriate information and counselling patients about the rationale, benefits, and limitations of testing and any impact on their current or future treatment will also be a key role for pharmacy staff, who are already well-versed in talking to people about their medicines.

This will undoubtedly represent a significant change in practice, but one which all pharmacy professionals should be well placed to adopt and deliver with confidence.
GeNote Update: Supporting Clinical Decision-Making via the PROGRESS Study
Phase II of the PROGRESS study is now actively expanding across England, bringing pharmacogenetic clinical decision support (CDS) directly into GP practices nationwide. For more information on the study, please visit here: https://www.nw-gmsa.nhs.uk/about-us/our-projects/spotlight
This innovative integration ensures that tailored, gene-informed prescribing guidance becomes an accessible part of patient care, directly within GP records.
Each guidance notification includes project-developed insights, with an embedded section where healthcare professionals can learn more and access additional resources. Within this section, users will find direct links to relevant GeNotes pharmacogenomics resources, designed to support in-the-moment clinical decisions.
For instance, if prescribing guidance for statins is prompted based on a patient's genetic profile, practitioners will be provided with a link like this: Patient with known SLCO1B1 genotype requiring statin therapy.
Explore these resources further to enhance your understanding and support clinical decisions with pharmacogenomic insights: GeNotes Pharmacogenomics Resources.
A Frequently asked questions (FAQ) document has been developed by the project team and is available via NHS Futures.
Advancing the application of pharmacogenomics via digital innovation; introducing ProgressRX
Almost half of all UK adults regularly take prescription medicines and the annual NHS budget for medicines is approximately £17.4 billion per year, with over 1.1 billion items prescribed annually.
Medicines are the most common therapeutic intervention in healthcare, yet the efficacy and safety of many drugs show considerable interpersonal variation; some patients have been prescribed medication that does not work well, while others develop reactions to their medicines.
One approach to addressing adverse or ineffective medication reactions is to use knowledge of an individual’s genetic information to support medicines optimisation, better informing medicine selection and dosing, a concept known as pharmacogenetics.
Pharmacogenetics is the study of genetic causes of individual variations in drug response, whereas Pharmacogenomics (PGx) is the study of how variations in the human genome dictate a person's response to medications, and how we can leverage the knowledge of an individual’s genetic information to support medicines optimisation, better-informing medicine selection, and dosing.
The North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance are leading on the national Pharmacogenomic and Medicines Optimisation NHS Genomic Network of Excellence across England, supporting the roll out of pharmacogenomics (PGx) and medicine optimisation across the NHS.
The Pharmacogenetics Roll Out – Gauging Response to Service [PROGRESS] programme is an NHS England (NHS E) funded transformation project led by researchers at Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust (MFT) and the NHS NW Genomic Medicine Service Alliance (NWGMSA), to investigate the feasibility of delivering pre-emptive pharmacogenetic panel testing in primary care in the NHS.
A key element of the study is the development of a digital proof of concept which translates genetic test results into prescribing advice, within a primary care setting.
Introducing ProgressRX
ProgressRX harnesses the power of pharmacogenomic data, as an ‘end-to-end diagnostic interpretation tool’ which uses existing NHS clinical data systems.
Initial trials are currently taking place within primary care, which have proven where ProgressRX has bridged the gap between the interpretation of genomic test data, and enhanced prescribing practice, without increasing cognitive burden on the prescriber.
By streamlining the integration of pharmacogenomic data into existing clinical decision support (CDS) systems, ProgressRX is a technological milestone which embodies the collective efforts of stakeholders committed to advancing genomic medicine and delivering superior patient care.
How does ProgressRX work?
- It provides real time PGx guidance, for prescribers/practitioner with clinical safety paramount.
- It maximises access and utilisation of available pharmacogenomic data, supports and harnesses existing NHS clinical decision support (CDS) systems.
- CDS systems are digital tools that can support clinicians to make equitable, evidence-based decisions. They can be used across care settings, specialties, and pathways to improve healthcare delivery and reduce errors.
- Transformation of healthcare services with CDS requires consideration of several critical success factors – encapsulated by the six Is: inclusive, intelligent, interpretable, integrated, impactful, interoperable.
- Genomic test results are interpreted and kept, to inform the prescribing process within General Practice, Primary Care Pharmacy, Mental Health Trusts, and Acute Hospital settings.
- If no PGx guidance needed, then no message is generated. There is no added cognitive burden on the prescriber/practitioner.
- The service uses the individuals’ NHS number to ensure that the correct patient is found.
- Guidance is tailored to individual patients, in line with their genomic data, for all prescribing events.
- ProgressRX has been developed in line with the national Unified Genomic Record (UGR) which is a virtual case note, and enables the collation of genomic data, to develop a single genomic profile which can be managed and updated over a lifetime, whilst ensuring compatibility and interoperability across healthcare settings.
- The digital service is hosted in the NHS cloud which seamlessly integrates with existing clinical decision support systems which currently provide pharmacogenomic guidance ‘natively.’
Through strategic partnerships and collaborative efforts, ProgressRX is poised to set a new standard for genomic medicine services, driving innovation and enhancing patient care on a regional and national scale.
Key partnerships
With trials underway at selected sites, the potential of ProgressRX to optimise medication utilisation and improve patient outcomes becomes increasingly clear.
Moving forward, ProgressRX will be evaluated across existing systems to optimise and migrate existing genetic information, supplying longevity to the individuals’ genetic profile.
Collaborative working and digital innovation are at the heart of the project, in support of effective implementation of an informatic solution, a single version of the truth, which can communicate the results of pharmacogenetic testing, without adding added burden to professionals at the point of care. The project not only showcases technological innovation but also highlights the collaborative efforts of various stakeholders in advancing enhanced patient care in the North West and beyond.
Professor Bill Newman, Consultant in Genomic Medicine at MFT and Clinical Director, NHS North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance said: “At its core, pharmacogenetics uses individual genetic information to guide medication selection and dosing. This tailored approach to medicine optimization holds immense promise for personalised patient care.
Professor Newman, who is also Rare Conditions Co-Theme Lead at the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Manchester Biomedical Research Centre (BRC), added; “For the implementation of pharmacogenetics within healthcare to be effective, an end-to-end service like ProgressRx which links testing to prescribing needs to be developed and embedded in practice”.
Scott Watson, Genomics Informatics Director, NHS North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance added: “Traditionally, genomic testing has been siloed within healthcare systems, with results often confined to specific platforms or geographical boundaries. This fragmented approach not only limits the sharing of valuable genetic insights but also places a significant cognitive burden on prescribers, who must interpret results for each prescribing event.
“Trials are currently underway at selected sites, building upon first discovery work, which is an exciting prospect given ProgressRX’ s ability to integrate with existing CDS, to optimise the utilisation of pharmacogenomic data for patients and prescribing decisions.
“The feasibility study for ProgressRX has shown that the service enhances patient care, but also supplies significant cost efficiencies in relation to medicine optimisation”.
Dr David Lewis, GP, Vauxhall Health Centre, Liverpool said: “This is a fantastic study, and we are delighted to be involved. Pharmacogenomics may improve prescribing as it will help us give people the right dose of the right drug for them. As a digital proof of concept, ProgressRX enables prescriptions to be tailored to the individual, informed by their genetic test results.
“Hopefully in the future anyone who chooses can give a saliva sample once in their life, and then whenever they start or change medication, their prescriber will have easy access to information to guide the best choice of drug for that person”.
Ends
About Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust
Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust is the largest NHS Trust in the country and a leading provider of specialist healthcare services. Its ten hospitals are home to 28,000 staff including world class clinicians and academic staff committed to finding patients the best care and treatments. Its hospitals are Manchester Royal Infirmary, Saint Mary's Managed Clinical Service, Royal Manchester Children's Hospital, Manchester Royal Eye Hospital, University Dental Hospital of Manchester, Trafford General Hospital, Altrincham Hospital, Wythenshawe Hospital, Withington Hospital and North Manchester General Hospital. More information is available at www.mft.nhs.uk
About the North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance
The NHS North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance (NW GMSA) is one in a network of seven regional alliances launched in England in January 2021 by the NHS Genomic Medicine Service (GMS) to oversee and co-ordinate the embedding of genomics into routine healthcare across England. In October 2022, NHS England published Accelerating Genomic Medicine in the NHS, the first NHS genomics strategy, which included the establishment of eight ‘NHS Genomic Networks of Excellence’ to develop the evidence and model of adoption for cutting edge genomic advances and technology applications that will be transformative for patients. The networks of excellence sit within the existing network of Alliances, across England. More information is available at www.nw-gmsa.nhs.uk
Personalised medicine in action: PROGRESS study advances to Phase II
The PROGRESS project, a national pharmacogenomics research study, is transforming primary care by incorporating genetic insights into everyday prescribing practices across England.
Pharmacogenomics uses genetic information to improve medication safety and effectiveness, reducing adverse drug reactions and enhancing patient outcomes. The PROGRESS study is at the forefront of exploring how pharmacogenomic testing can be implemented in primary care and expanded across the NHS.
This project is supported by the NHS England Genomics Programme through the Pharmacogenomics and Medicines Optimisation Genomic Network of Excellence, led by the NHS North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance.
Following the success of Phase I and the launch of Phase II, the study is delivering valuable insights and making significant progress towards adopting personalised medicine within the NHS.
Phase I achievements
Recruitment and demographics
Phase I of the study exceeded expectations, enrolling over 250 participants in the North West of England. These participants represented a wide range of ages and ethnicities, reflecting the demographics of the local population.
Participants ranged from 18 to 92 years old, with particularly strong engagement from young adults aged 20 to 24 and seniors aged 65 to 69. Most were recruited based on prescriptions for statins (drugs that can lower your cholesterol) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)—a commonly prescribed type of antidepressant—demonstrating the value of pharmacogenomics for these widely used medicines.
Impact on patients
Preliminary results showed that 28% of participants received pharmacogenomic recommendations that altered prescribing decisions. This highlights the significant potential of genetic testing to improve both medication safety and effectiveness.
Innovation through eConsenting
Challenges in integrating research into busy primary care settings were addressed through the introduction of eConsenting, which allowed patients to provide consent remotely. This innovation, combined with direct sample submission to the NHS North West Genomic Laboratory Hub, led by Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust (MFT) made the process more efficient and reduced delays.
Phase II expansion
Phase II is broadening the study’s reach, with recruitment now extending across England. This phase also introduces ProgressRx, a cutting-edge digital tool designed to integrate pharmacogenomic results directly into prescribing systems.
What is ProgressRx?
ProgressRx is an "end-to-end diagnostic interpretation tool" that seamlessly translates genomic test results into practical prescribing advice. It integrates into existing NHS clinical decision support (CDS) systems, reducing the cognitive burden on prescribers while providing real-time, patient-specific guidance.
CDS provides timely information, usually at the point of care, to help inform decisions about a patient's care. CDS tools and systems help clinical teams by taking over some routine tasks, warning of potential problems, or providing suggestions for the clinical team and patient to consider.
Key features of ProgressRx include:
- Real-time guidance: Informs prescribing decisions using individual genetic data without disrupting workflow.
- Interoperability: Works with the national Unified Genomic Record (UGR), creating a single, lifelong genomic profile for each patient that can be accessed across healthcare settings.
- Seamless integration: Hosted in the NHS cloud, it aligns with existing CDS systems to support fair, evidence-based decision-making.
Transforming patient care
By tailoring prescriptions based on genetic insights, ProgressRx reduces the risk of adverse drug reactions, hospital admissions, and ineffective treatments. It also delivers cost efficiencies by optimising medication use, making it both a patient-centred and economically sustainable solution.
A vision for the future
The PROGRESS project is addressing barriers to the national implementation of pharmacogenomics, paving the way for personalised medicine to become standard practice.
Through collaboration with enabler stakeholders ProgressRx exemplifies innovation in action.
Trials at selected sites have shown its seamless integration into primary care, and existing primary care clinical decision systems (CDS), reiterating the opportunity and potential for a nationwide rollout.
As Professor Bill Newman, Clinical Director of the NHS North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance and Consultant in Genomic Medicine at MFT, and national lead for the PROGRESS research study explained: “For pharmacogenetics to be successfully embedded in healthcare, an end-to-end service like ProgressRx, which links testing to prescribing, is essential.
“With ProgressRx and the insights from the PROGRESS study, the NHS is poised to take a bold step towards personalised medicine, improving outcomes for millions of patients across England,” he added.
About the PROGRESS project
The PROGRESS project is an NHS England-funded initiative led by Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust and the NHS North West Genomic Medicine Service Alliance. It supports the national rollout of pharmacogenomics and medicines optimisation across the NHS, ensuring that innovative genomic medicine is accessible to all patients.
More information in relation to enabler stakeholders can be found on our website: https://www.nw-gmsa.nhs.uk/about-us/our-projects/genomic-networks-excellence/pharmacogenomics-and-medicines-optimisation-genomic-network-excellence
Genomic information has the potential to transform healthcare by predicting disease, personalizing treatments, and enhancing patient care and experience. However, current testing methods are often too slow and lack the necessary precision to be widely used in clinical settings.
To unlock the potential of advanced diagnostics, it is crucial to develop technologies capable of delivering clinically relevant genetic information within the required timeframes.
By harnessing Greater Manchester’s leading academic expertise in genomics and its growing Biotech ecosystem, Professor Bill Newman, Dr. John McDermott, and Dr. Videha Sharma have developed an innovative translational pipeline. This unique approach enables the creation of rapid genomic tests through the establishment of new partnerships across a wide range of domains. These partnerships support both academic and industry collaborators through various stages of development.
The DEVOTE Programme is a collaboration between industry, universities, and healthcare professionals, in support of the development and implementation of time-critical genomic testing technologies. The programme links with PROGRESS, in relation to identifying how pharmacogenetics can be used to improve patient outcomes when they need treatment with common medicines like anti-depressants and statins.
Significant funding has been secured which builds on the successful PALOH study where Professor Bill Newman and colleagues, working in collaboration with Genedrive, showed that point-of-care genetic testing could be used in neonatal units to prevent babies from losing their hearing.
The programme has established eight distinct expertise domains, each representing a specific area of knowledge and skills. By bringing together specialists from these domains, DEVOTE fosters collaboration and innovation, ensuring scientific discoveries can be translated more effectively and efficiently into tangible improvements in patient outcomes.
https://healthinnovationmanchester.com/our-work/devote/
